parallel algorithm course 10
final exam
review
- fundamental
DAG
work-span analysis
- ideal: \(T_1(n)=T_s(n)\), \(T_\infty(n)=\Theta(\log^k(n))\)
only consider shared data memory model
algorithm:
- map: n->n
associative
reduce:n -> 1
scan: n -> n
- compact: n -> m
list ranking: n -> n, input becomes linked list, GRAPH, BFS, DFS, find independent
sorting, sample sort
goal:
optimal complexity
independent ++, sync –, don’t use sync too much, has cost, e.g. print message during parallel
e.g. histgram, lock in each bucket
symetrics –, repeat occurance, break symetric, use randomize
thinking:
case to general
forward - backward, cover gap between input and output
bit-wise, radix sort
matrix-wise, compute fibonacci sequence, matrix operation
pattern
divide & conquer
indep set
random
jump
Eulur tour
Bag of pennants (conform divide and conquer patterm)
openacc
profile driven programming
analyse
parallel
optimize
incremental programming
CPU -> GPU -> Unified memory -> data parallel -> loop -> blocking
blocking:
IO and compute parallel
multi-device
Analyse
observe profile
bottle-neck, for loop
improve \(\frac{\text{compute}}{\text{mem}}\) access ratio
Parallel
- algorithm
Optimize
data movement, manual management
large matrix, sometimes we don’t need load all the elements
loop mapping: tell compile how loop maps the level of parallel, e.g. vetor length
vector 32*n -> n warps
blocking, 流水线并行
input compute output
compute -> futher split -> multi device
tile <- GPU 2-level cache usage
collapse
memory access pattern, keep continuous access
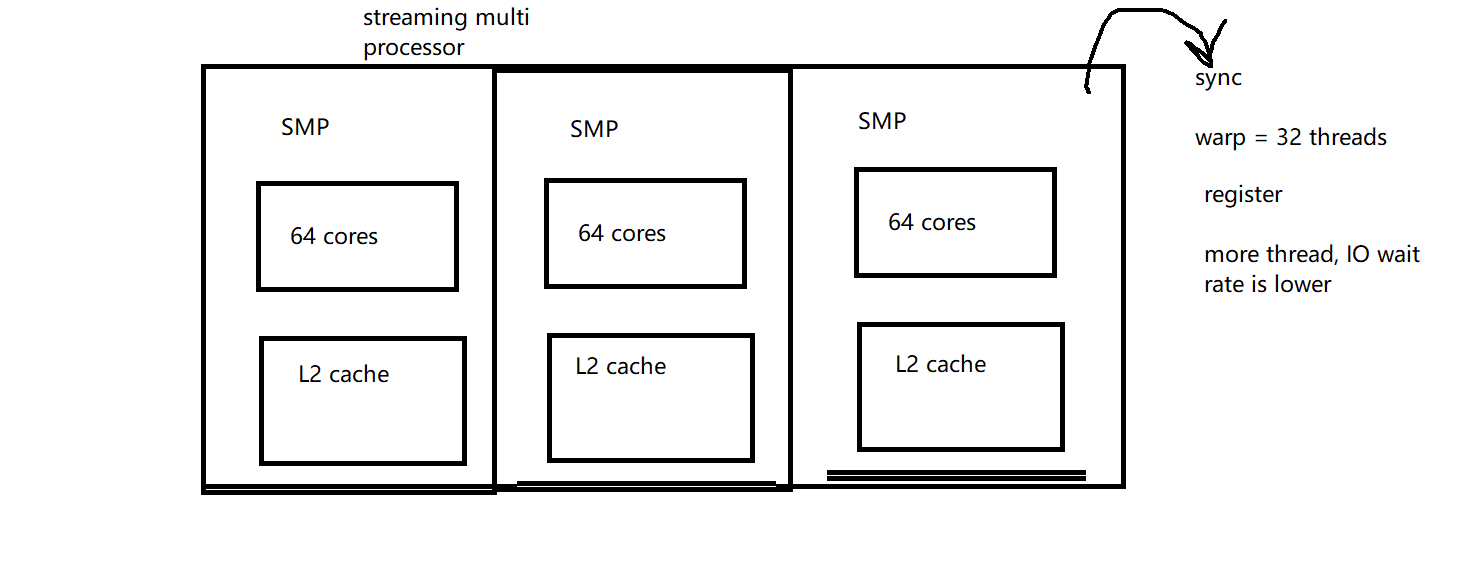
GPU hardware
简答题 X 2
算法题
期中前 X 1
期中后 X 1
编程题 X 1